

Cord swelling is usually present in the acute phase. Spinal cord involvement is extensive, with high T2 signal spanning at least three vertebral segments, often many more (known as a longitudinally extensive spinal cord lesion) 4,5,8,11. Often vanish but cystic change is seen in a minority of cases 13 May be more common in children and in patients from the Far East and Africa Limited if any mass effect although tumefactive lesions do occur 13 Radially oriented (spilled-ink appearances) or spindle-shaped Larger >3 cm diameter hemispheric white matter lesions The splenium may be diffusely involved and expandedĭeep (or less frequently subcortical) punctate white matter lesions (which may appear similar to those seen in MS)Ĭorticospinal tract involvement by extensive longitudinal lesions has been reported more frequently in Korean patients 5 Multiple callosal lesions with heterogeneous signal leading to a marbled pattern 7 Periventricular (hemispheric) confluent smooth sessile white matter involvement (unlike MS, there are usually no Dawson fingers) Lesions which mirror the distribution of aquaporin 4 in the brain, which is particularly found in the periependymal regions abutting the ventricles: These can be divided into four categories 5,8,13: Optic nerves appearing hyperintense and swollen on T2 weighted sequences and enhancing on T1 C+īilateral optic nerve involvement and extension of the abnormal signal posteriorly as far as the chiasm is particularly suggestive of NMO 5Ītrophy of the optic nerves with associated hyperintensities on T2 weighted sequences may be seen in chronic stages of the disease 11Īlthough traditionally NMO was thought to have normal intracranial appearance it is increasingly evident that asymptomatic abnormalities are present in the majority of seropositive NMOSD patients. Targeted imaging of the orbits (including fat-saturated T1 C+ and T2 weighted sequences (see MRI protocol: orbit) may demonstrate typical features of optic neuritis: MRI is the modality of choice for NMOSD and the orbits, brain and spinal cord should be imaged in suspected cases. These individuals appear to have somewhat different demographics and less severe clinical course and are increasingly considered to be afflicted by a distinct disorder ( MOGAD) that has clinical similarities to NMOSD 16,18. Generally, the condition is sporadic, although some overlap in immunogenic features between certain viruses and aquaporin-4 water channel have been identified 8.Ī significant proportion of individuals presenting with NMO but without AQP4 antibodies will be found to have anti-MOG IgG antibodies 16. Another differentiating feature is that axonal damage precedes demyelination in NMO 5. Additionally, however, and relatively specific for NMO, these regions will also demonstrate extensive eosinophilic infiltration, perivascular deposition of immunoglobulins (especially IgM) and local activation of the complement cascade 3. periaqueductal grey matter) which are particularly rich in aquaporin 4 8.Įarly in the disease, demyelinating regions will demonstrate similar findings to MS, such as macrophage/microglia activation and axonal damage. This accounts for some of the predilection for the circumventricular organs (e.g.
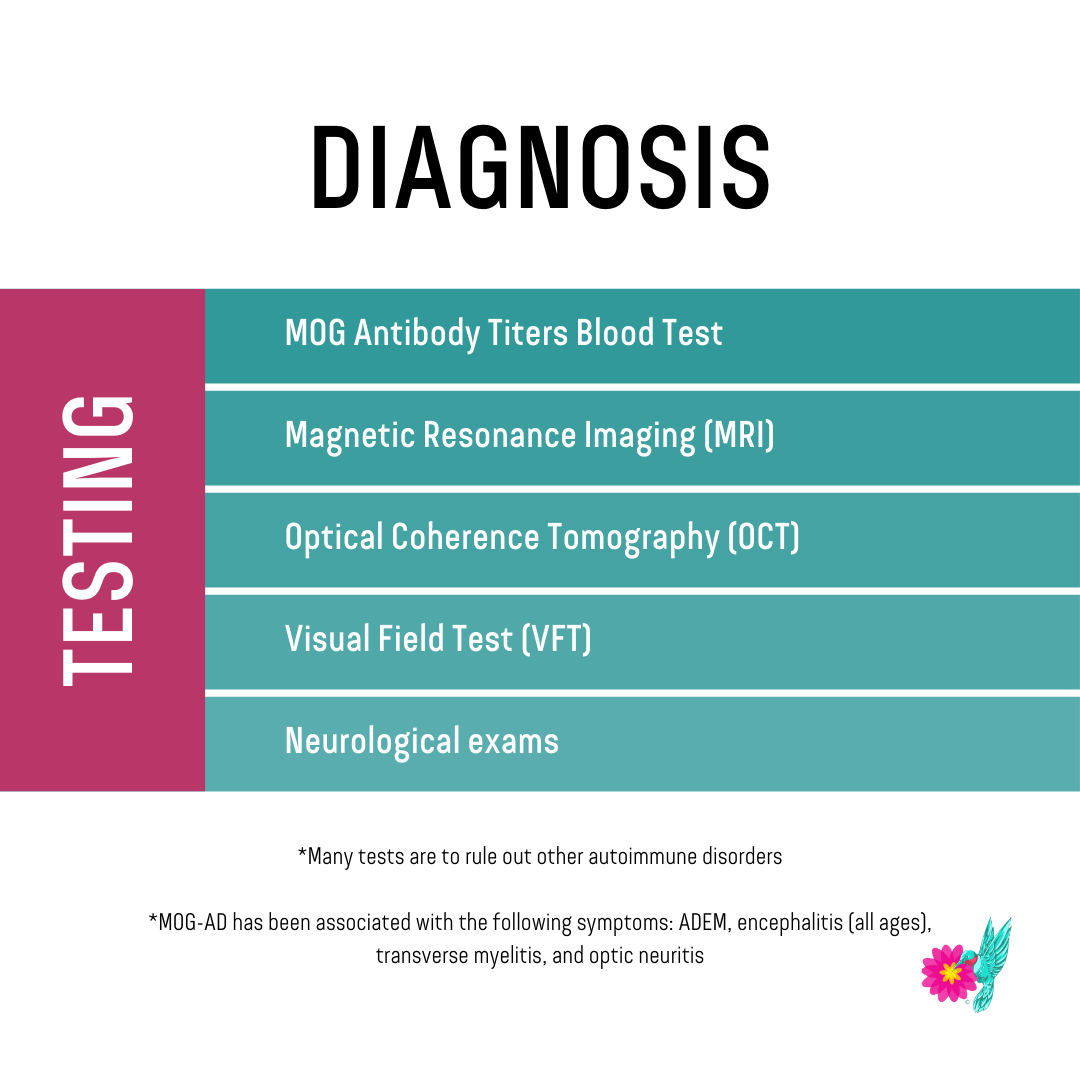
In approximately 70% (sensitivity of 70-90% specificity of 90%) of patients with established NMO, a specific immunoglobulin can be isolated (AQP4-IgG which targets a transmembrane water channel ( aquaporin 4) present on astrocyte foot processes abutting the limiting membrane 5,8. The current diagnostic criteria are defined by the International Panel for NMO Diagnosis. Additionally, it is now recognized that some patients present with unilateral optic nerve involvement.Īlthough NMO was initially thought of as a monophasic illness, it is now evident that, as with MS, it is usually a relapsing-remitting disease with symptomatic events separated by many years 5.įurthermore, NMOSD also encompasses non-neurological manifestations in anti-AQP4 antibody seropositive patients including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and Sjögren syndrome 13. Although the two usually present concurrently, it is not uncommon for one to precede the other by up to several weeks 3. NMO is characterized by bilateral optic neuritis and myelitis resulting in blindness and paraplegia. It is found more frequently in patients of Asian, Indian, and African descent 8. Neuromyelitis optica is typically found in patients somewhat older than those with multiple sclerosis (MS), with an average age of presentation of 41 years, and there is an even stronger female predilection (F:M 6.5:1) 6,8.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
